Postman for API testing and calling
In this section, we’ll introduce you to Postman, a powerful tool for testing and calling APIs. Postman is an API client that makes it easy for developers to create, share, test and document APIs. With this open-source solution, users can create and save simple and complex HTTP/s requests, as well as read their responses. We mainly use Postman for doing testing and calling end points.
We’ll provide guidance on its installation, the importance of using it, and how to conduct API calls, including examples. Additionally, we’ll cover the distinction between different hosts, handling headers, and accessing public APIs for testing.
- Postman Installation Link
-
-
Download Required: (Postman Application)
-
Online: (Postman Web)
-
Please register an account using XXX@wavelet.net email.
-
Learn how to make API calls in Postman from here.
- There are three types of hosts in the API URL paths that will be used
-
-
Local (hosted on local machine): localhost:5000
-
Staging (hosted on akaun.cloud): api.akaun.cloud
-
Development (hosted on akaun.dev): api.akaun.dev
-
For more on API Urls visit (API host and URL)
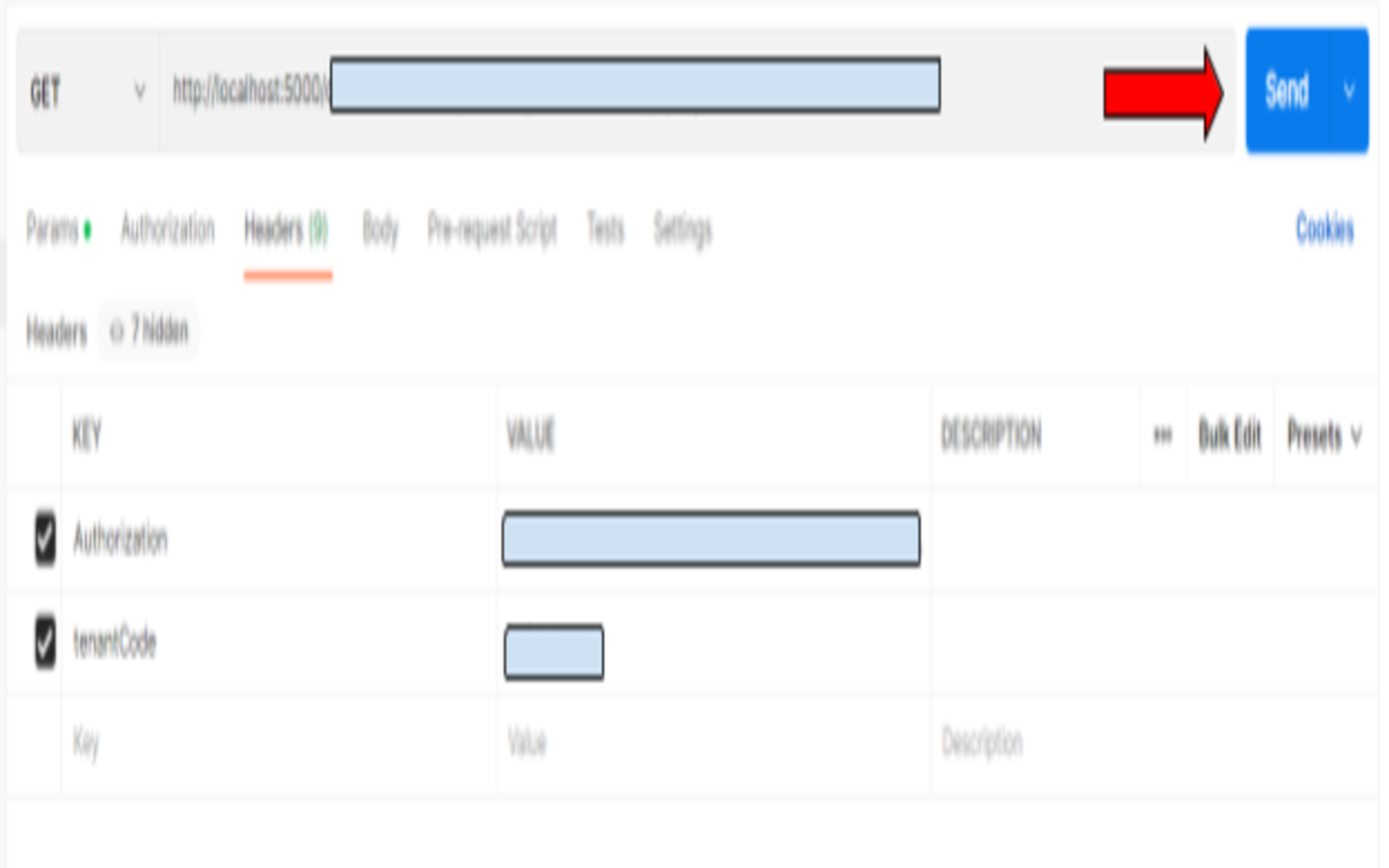
- When we need to call the URL endpoint, we MUST put Authorization and tenantCode in the Header
-
Most of the API calls in akaun require these two header parameters:
-
Authorization: This is an auth token that helps verify the person making the api request. To get you auth token, in the correct website: Inspect > Application > Local Storage(authToken).
-
Staging: akaun.cloud
-
Development: akaun.dev
-
-
tenantCode: This is the code for a particular tenant it helps identify which tenant database you are making the API request to. You might be familiar with this when you created a tenant in the app_generic_resources_hdr table and provided it a code while setting up the database earlier.
-
Example API call with Postman
GET request:
-
Add the headers for the API request. Place the URL for the API in the text field. Then select the http request method.
-
We can also add key value pairs as request parameters. Some API have additional fields that we can specify to get a particular response. This is done through the "Params" tab.
-
Proceed to send
-
Postman Tips
-
When calling APIs to localhost on Postman make sure that the URL you are using is HTTP and not HTTPS.
-
To test out some APIs on Postman use the following APIs, they are public APIs meaning that anyone can make the call without giving authorization credentials as part of the API request.
-
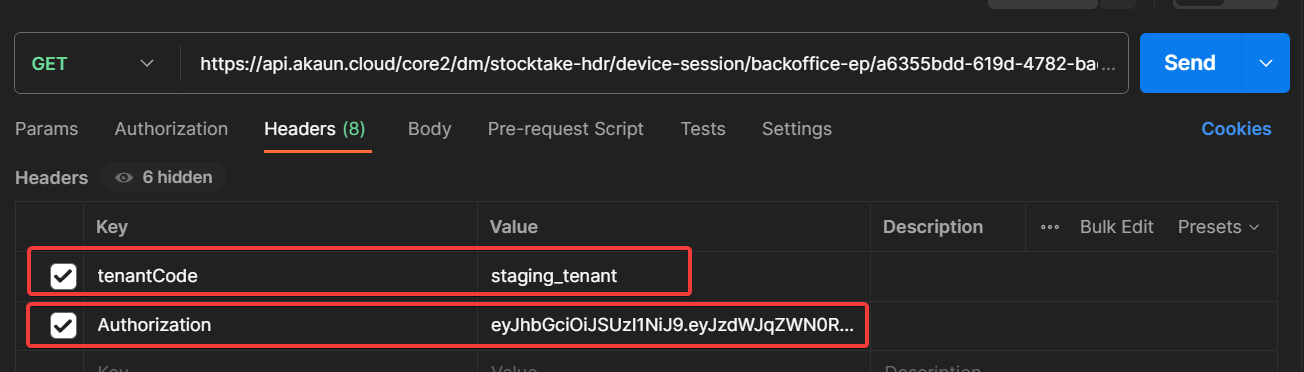
https://api.akaun.cloud/core2/tnt/dm/cms/widget-instances/public-ep - This is a GET public end point. Use this URL directly in Postman, in the headers tab place "tenantCode" as the key and "staging_tenant" as the tenant code. staging_tenant is the tenant database for the akaun.cloud testing environment. Once you send the request you should see the response of the request and the status of the response as "200 OK" meaning that the request was successful.
-